Logical operator in C
Relational operators are used to compare between two operands. However, relational operators does not support comparison of three or more quantities.
For example, suppose you need to check range of a number. You need to check whether a number n is in between 1-100 or not. For that you must check two conditions, first check if n > 1 finally check if n < 100.
Logical operators are used to connect two or more expressions as a singal expressioin. It returns boolean value either true (1) or false (0) depending on the given expression.
There are three logical operators in C.
| Operators | Description |
|---|
&& | Logical AND |
|| | Logical OR |
! | Logical NOT |
Logical AND (&&) operator:
We use logical AND operator in situations when two or more conditions must be true for a decision.
Logical AND (&&) operator is a binary operator. It returns true (0) when both the conditions are satisfied. Otherwise it returns false (1).
For Exmaple:
- #include <stdio.h>
- int main()
{
int x = 6, y = 3;
- if (x < 10 && y > 2)
printf("True, since both the conditions are satisfied.");
- else
- printf("False, since both the conditions are not satisfied.");
- return 0;
- }
Logical OR || operator:
Logical OR || operator is a binary operator. It returns true (1) even if one (or both) of the conditions is satisfied. Otherwise it returns false (0).
For Example:
- #include <stdio.h>
- int main()
{
int x = 6, y = 3;
- if (x > 10 || y > 2)
printf("It returns true, since 2nd condition is satisfied.");
- else
- printf("It returns false, if both conditions are not satisfied.");
- return 0;
- }
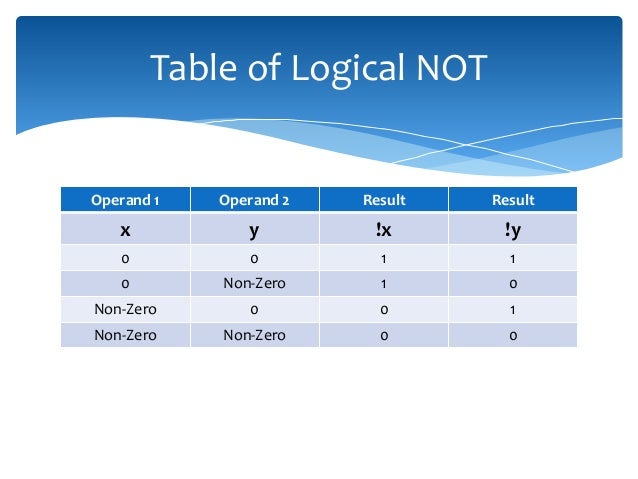
Logical NOT ! operator:
Logical NOT ! is a unary operator it has only one operand. It is used to reverse the logical state of its operand. In other words, if a condition is true, then logical NOT operator will make it false.
For Example:
- #include <stdio.h>
- int main()
{
int x = 6, y = 3;
- if (!(x == y))
printf("It returns true, since x!=y condition is satisfied.");
- else
- printf("It returns false, if both conditions are not satisfied.");
- return 0;
- }











Help others by sharing this page.

Ahmad Irshad
Author & Editor
I love blogging, teaching, learning computer science and sharing it to others. I've written and develped this site so that students may learn computer science related tutorials eaisly. MCA / MCITP
Wednesday, July 08, 2020
C















0 Comments:
Post a Comment
Please don't enter any spam link in the comment box.