We learned about Continue statement in previous tutorial. In this tutorial, we will learn to use of break statement with the help of examples.
- Flow Chart of break Statement?
- Example 1: break in a for loop
- Example 2: break in a for loop
- Example 3: break in a while loop
- Example 4: break in do...while loop
- Example 5: break statement in switch...case
- Read more bout
Quick links:
How does a break Statement work in C?
- The break is a keyword in C, which is used to bring the program control out of the loop. When a break statement is encountered inside a loop, the control directly comes out of loop and the loop gets terminated. It is used with if statement, whenever used inside loop.
- This can also be used in switch case control structure. Whenever it is encountered in switch-case block, the control comes out of the switch-case(see the example below).
Syntax:
//loop or switch case
break; Flow Chart of break Statement:
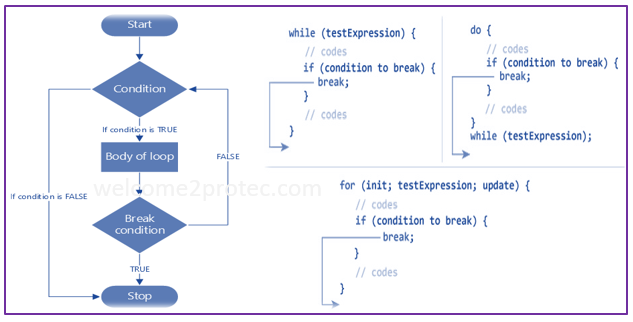 |
| Flow chart of break statement in C | welcome2protec.com |
Example 1: break in a for loop
#include <stdio.h>
#include <conio.h>
void main ()
{
int num, i;
clrscr();
printf("Enter any number between 1-100:");
scanf("%d", &num);
for(i = 1; i < 100; i++)
{
printf("%d\n", i);
if(i == num)
break;
}
printf("Loop skipped since i == num");
getch();
} Output
Enter any number between 1-100: 5
1
2
3
4
5
Loop skipped since i == numExample 2: break in a for loop
/* Program to check to accept 10 nos from user
* but if no entered is greater than 100, exit */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <conio.h>
void main ()
{
int x, i;
clrscr();
for(i = 1; i <= 10; i++)
{
printf("To exit for loop you must enter no > 100: %d\n", x);
scanf("%d ", x);
if(x > 100)
break;
else
printf("Now loop is terminated since, you've entered no > 100: %d\n", x);
}
getch();
} In above, If at any point of time, the user enters no greater than 100, the for loop is terminated, even if the iteration are left.
Output
Now loop is terminated since, you've entered no > 100: 105Example 3: break in a while loop
#include <stdio.h>
void main ()
{
int i = 1;
while(1)
{
printf("%d ",i);
i++;
if(i == 10)
break;
}
printf("loop skipped since condition (i==10) is returned true");
} Output
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 loop skipped since condition (i == 10) is returned trueExample 4: break in do...while loop
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int n = 10;
do{
printf("n = %d\t", n);
n = n-1;
if(n == 5)
break;
}while(n > 0);
printf("\nOutside loop");
return 0;
}Output
n = 10 n = 9 n = 8 n = 7 n = 6
Outside loop#include <sdtio.h>
int main(){
int number=0;
printf("enter a number:");
scanf("%d", &number);
switch(number){
case 10:
printf("number is equals to 10");
break;
case 20:
printf("number is equal to 20");
break;
case 30:
printf("number is equal to 30");
break;
default:
printf("number is not equal to 10, 20 or 30");
}
return 0;
} Output
Output 1:
enter a number:4
number is not equal to 10, 20 or 30
Output 2:
enter a number: 20
number is equal to 20- goto statement
- Continue statement
- Switch-Case statement
- Control statement















 Computer quiz for competitive exams | Bank, PO, SCC and many more...
Computer quiz for competitive exams | Bank, PO, SCC and many more...
0 Comments:
Post a Comment
Please don't enter any spam link in the comment box.